Clinical Thermography, otherwise known as Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging, is based on a careful analysis of skin and tissue temperatures. It is a non-invasive screening procedure that allows practitioners to see where there is abnormal chemical and blood vessel activity in body tissue. It looks at blood flow patterns, inflammation and asymmetries, which can assess pain anywhere in the body or detect early warning signs for breast cancer long before you can feel a lump. Thermography is a comfortable, radiation free, non-compression and painless procedure. There is no contact with the body. Your thermal images are used by your healthcare practitioner to help diagnose and monitor pain or pathology in any part of your body. Thermography uses the technology of a medical grade infrared camera and state of the art software to achieve its images.
Thermography has the unique ability to “map‿the individual fingerprint of a woman’s breasts. Any change in this map over the course of months and years can signal an early indication of possible tumors or other abnormalities. In fact, studies have shown that an abnormal infrared image is the single most important indicator of high risk for developing breast cancer.
Thermography has many clinical applications including:
| • | To aid in the early detection of disease and pathology. |
| • | To help in determining the cause of pain. |
| • | To evaluate sensory-nerve irritation or significant soft tissue injury. |
| • | To define a previously diagnosed injury or condition. |
| • | To identify an abnormal area for further diagnostic testing. |
| • | To follow the progress of healing and rehabilitation. |
Over thirty years of clinical use and more than 8,000 peer- reviewed studies in medical literature have established thermography as a safe and effective screening tool. The procedure has been approved by the FDA since 1982. Thermography uses no radiation, compression or patient contact to achieve its images. Thermography is non-invasive, painless and is safe for women who are pregnant, nursing or have breast implants.
Every woman should have breast thermography as part of her regular breast care. Thermography is especially beneficial in younger women, under age 50, because the breast tissue is more dense, which makes it difficult for mammograms to detect abnormalities or pick up suspicious lesions. Breast cancers are particularly aggressive in younger women and, according to the American Cancer Society Breast Cancer Guidelines, approximately 15% of all breast cancers occur in women under age 45. Breast cancers tend to grow significantly faster in younger women under age 50 and have lower recovery rates. Unfortunately, there are no clear guidelines for breast imaging in this age group.
Eighty percent of women who develop breast cancer have no prior family history or risk factors. With the addition of breast thermography, women have another tool that they can add to their regular preventative breast checkups and they can safely start getting thermograms at any age. Prevention is the gold standard of health care and with thermography, every woman can have the opportunity to be proactive in her breast care without the fear of radiation exposure or effects of compression.
| AGE | AVERAGE TUMOR DOUBLING TIME |
| Under 50 | 80 days |
| Age 50 – 70 | 157 days |
| Over age 70 | 188 days |
| Source: Cancer 71:3547-3551, 1993 | |
The faster a malignant tumor grows, the more Infrared radiation it generates. For younger women in particular, results from a thermal scan can lead to earlier detection and, ultimately, a longer life.
Doctors do not yet know how to prevent breast cancer. However you can increase your chances of detecting breast cancer in its earliest stages by understanding the need for, and participating in an early detection program.
Only about 20 percent of biopsied breast lumps are cancerous. And, if cancer is found early, there are choices for treatment. With prompt treatment, the outlook is good. In fact, most women treated for early breast cancer will be free from breast cancer for the rest of their lives.
Please fill out all patient forms prior to your appointment, including the HIPPA authorization form. These can be printed from our Home page under “Patient Forms�?If you are unable to print these forms, we will have them available to fill out in our office on the day of your appointment. Plan to arrive 10 to 15 minutes early to complete all forms. If you would like a copy of your thermography results sent to your healthcare provider, please provide us with the name and address of you healthcare provider on the day of your visit.
Thermography is a temperature gradient study. To achieve optimal images, we do not want to create or block the natural heat of the body. Please follow these general instructions:
*No powder, lotion, creams, deodorant, antiperspirants or liniments on the day of your test.
* No makeup if the face will be imaged.
*No shaving (or other types of hair removal) of the chest, breasts or underarms 24 hours prior to the exam.
*No smoking for a minimum of 2 hours before the test.
*No excessive hot or cold drinks prior to the test.
*If bathing, it must be no closer than 1 hour before the exam.
*If you are nursing, please try to nurse as far from 1 hour prior to the exam as possible.
*Do not have massage, physical therapy, TENS, electrical muscle stimulation, hot or cold pack use, acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments or electromyography for 24 hours prior to your exam.
*No physical stimulation of the breasts 24 hours prior to the exam.
*No vigorous exercise 4 hours prior to the test.
*Stay out of strong sunlight on the day of your test. No prolonged sun exposure (especially sunburn) or tanning beds for 5 days prior to the exam.
*Long hair should be worn up. Hair accessories will be provided, but feel free to bring your own hair clips or holders.
*Jewelry and glasses will need to be removed if they are worn in the areas to be imaged.
*Please wear loose fitting clothing.
There are no dietary or medication restrictions.
Thermal images can be taken of the whole body or individual regions, including the breasts, head, arms, legs and torso. A lumbar assessment would typically include, low back, pelvis and legs. A cervical assessment would typically include, head and neck, upper trunk and arms. Our services include full body scans, half body (upper body or lower body), breast or a specific region of interest.
No, because Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging is radiation-free and a completely safe procedure, no prescription or referral is needed.
Our Digital Infrared Thermal Images are taken by a Certified Clinical Thermographer that has been trained and certified by the American College of Clinical Thermology. The ACCT is a professional body with an approved code of ethics and practice protocols that include quality control guidelines.
We use a sophisticated, medical grade, infrared camera to produce high-resolution diagnostic images of temperature and vascular changes. Our camera is designed specifically for clinical applications and delivers a higher degree of sensitivity and specificity than any other system. The digitized images are sent electronically to a central data-base where a physician will interpret the images and perform statistical analysis.
A female thermographer will be performing all of your imaging at Ohio Infrared Health.
Digital Infrared Thermal Images are interpreted by our team of Board Certified Medical Doctors that are clinically trained as Thermologists and are highly experienced in the diagnosis and protocols of thermal images. Our Medical Doctors are available to consult with your health care provider regarding your image results. All of your images will be kept on record for comparison with future images.
There are simple preparation instructions that must be followed on the day of your imaging, before you arrive. These instructions are explained above under “What do I have to do to prepare for a thermal scan�?/p>
Once in our office, you will be given privacy to disrobe into a gown. All jewelry and clothes must be removed in the areas to be scanned. Underpants may be worn for a full body scan. For a breast scan, you will undress from the waist up. The Thermographer will go over your health history forms with you and at that time she will also explain the procedure. You will then be positioned in front of the imaging system. It will take about 15 minutes to complete images of the breast or a specific region of interest and approximately 30 minutes for full body imaging. After the images are complete, the Thermographer will show you the images and answer any questions.
The images are sent electronically through a secure data system for interpretation by a medical doctor that is trained specifically in reading Digital Infrared Thermal Images. We will have the results in less than 48 hours, and in most cases under 24 hours. The doctor’s written report and a color copy of all of your images will be mailed to you the next business day from the time your report has been interpreted. We will also mail a copy to your doctor at no cost (please provide the name and address of your healthcare provider on the day of your visit). The images are archived in our system for comparison of future images so that the breasts or body areas of interest can be monitored over time. We are HIPPA compliant and will not share your information with anyone. If you would like your results sooner, we are able to expedite the interpretation of your results for a $15 fee.
Mammography, ultrasound, MRI and other structural imaging tools rely primarily on anatomy or structure, which means they can find a physical tumor or lesion once it is already present. Thermography is based on the body’s physiology or function. It detects the heat produced by increased blood vessel circulation and metabolic changes associated with a tumor’s genesis and growth. By detecting minute variations in normal blood vessel activity, infrared imaging has the ability to find thermal signs that suggest a pre-cancerous state, inflammation, or the blood flow patterns that could indicate the presence of an early tumor that is not yet large enough to be detected by physical examination (self breast exam), mammography or other imaging tools. The average cancer takes up to 8 to 10 years to become large enough to become visible on a mammogram, typically 3mm (the size of a pea) and inflammatory breast cancers do not show up on a mammogram, but can be detected with thermography. Active cancers begin creating a blood supply at about 1/5mm (the size of a pin head). Thermography’s ability to detect these early changes in blood supply makes it is possible for the earliest possible detection of breast disease, before a mass is large enough to be felt or seen on a mammogram. Combined with an unprecedented role in risk assessment, screening for younger women and radiation free, breast thermography offers women information that no other procedure can provide.
The faster a malignant tumor grows, the more heat it generates. For younger women in particular, results from DITI can lead to earlier detection and ultimately, a longer life. More than 90 percent of women diagnosed with early stage, localized cancer are alive five years later, yet only 58 percent of cancers diagnosed are at this stage, according to The American Cancer Society.
During a clinical breast exam, a physician must rely on touch and eyesight to detect tumors in the breast, which for women under age 50, may often occur when cancer is no longer localized or confined to the breast. DITI can provide an alert before clinical breast exam, referral to mammography, Ultrasound, or MRI so as to enhance early detection by the physician.
Difficulties in reading mammograms can occur in women who are on hormone replacement, are nursing, have breast implants or large, dense, fibrocystic breasts. These differences do not cause difficulties in reading Digital Infrared Thermal Images. DITI also captures the underarm area in the breast images, for a more thorough and complete screening than other tests provide.
| Mammography | Thermography | Ultrasound |

|
|

|
| Uses X-rays to produce an image that is a shadow of dense structures. Suspicious areas need to be dense enough to be seen. | Uses infrared sensors to detect heat and increased vascularity (angiogenesis) as the byproduct of biochemical reactions. The heat is compiled into an image for computerized analysis. | High frequency sound waves are bounced off the breast tissue and collected as an echo to produce an image. |
| Structural imaging. Ability to locate the area of suspicious tissue. | Functional imaging. Detects physiologic changes. Cannot locate the exact area of suspicion inside the breast. | Structural imaging. Ability to locate the area of suspicious tissue. |
| Early detection method. | Early detection method. Used as an adjunctive imaging test. | Low spatial resolution (cannot see fine detail). Good at distinguishing solid masses from fluid filled cysts. Used as an adjunctive imaging test. |
| Findings increase suspicion. Cannot diagnose cancer. | Findings increase suspicion. Cannot diagnose cancer. | Findings increase suspicion. Cannot diagnose cancer. |
| A biopsy is the only test that can determine if a suspected tissue area is cancerous. | ||
| Can detect tumors in the pre-invasive stage. | May provide the first signal that a problem is developing. | Ability to detect some cancers missed by mammography. |
| A positive infrared image represents the highest known risk factor for the existence of or future development of breast cancer �?0 times more significant than any family history of the disease. | ||
| Average 80% Sensitivity (20% of cancers missed), in women over age 50. Sensitivity drops to 60% (40% of cancers missed) in women under age 50. | Average 90% Sensitivity (10% of cancers missed) in all age groups. | Average 83% Sensitivity (17% of cancers missed) in all age groups. |
| Hormone use decreases sensitivity. | No known effect. | No known effect. |
| Large, dense, and fibrocystic breasts cause reading difficulties. | No effect. | No known effect. |
| In most women, the medial upper triangle, peripheral areas next to the chest wall, and the inframammary sulcus cannot be visualized. | Not applicable. | Not applicable. |
|
Sources: Index Medicus â€‿ACS, NEJM, JNCI, J Breast, J Radiology, J Clin Ultrasound Index Medicus â€‿Cancer, AJOG, Thermology Text â€‿Atlas of Mammography: New Early Signs in Breast Cancer Text â€‿Biomedical Thermology |
||
The most accurate result we can produce is change over time. Before we can start to evaluate any changes, we need to establish an accurate and stable baseline for you. This baseline represents your unique thermal fingerprint, which will only be altered by developing pathology. A baseline cannot be established with only one study, as we could not determine if this is your normal pattern or if it is actually changing at the time of the first exam. By comparing two studies 3 months apart, we are able to judge if your breast physiology is stable and suitable to be used as your normal baseline and safe for continued annual screening. The three month interval relates to the period of time it takes for blood vessels to show change; a period of less than 3 months may miss significant change, and a period of much more than 3 months may miss significant change that has already taken place. There is NO substitute for establishing an accurate baseline. A single study cannot do this. Once a baseline is established, we can continue with yearly screenings.
Yes, you will receive a copy of the doctor’s interpretation and a color copy of all your images in the mail. We will have your results back in less than 48 hours and in most cases less than 24 hours. Your report will be mailed the next business day after it has been received. We will also mail a copy of your interpretation to the healthcare provider of your choice at no additional cost.
Early detection is the key to a good outcome. Thermography is not diagnostic, but it does identify early risk factors. A biopsy is the only test that can determine if a suspected area is cancerous. An abnormal thermogram allows for therapeutic lifestyle changes to be incorporated and the ability to be monitored closely by your doctor, who will determine any further interventions with regard to your results. The interpreting doctor’s report will recommend if you should seek further investigation and what follow up should be done. The reports are straight forward and in medical format. Your health care professional may contact the medical doctor that interpreted your thermogram to discuss any abnormal findings or consult with them for any reason. Please note that the interpreting doctor cannot legally consult directly with the patient.
No, they complement each other. There is no competition between the two tests. Thermograms and mammograms are two separate tests that report different findings. Thermography is a test of physiology, while mammography is a test of anatomy. Thermography shows information relating to vascular activity, inflammation, lymphatic activity, hormonal dysfunction and other functional abnormalities. Thermography can detect the potential presence of a tumor up to 10 years before a mammogram can see it because it has the ability to detect inflammation and changes in blood vessel patterns that are the precursors to disease. Thermography does not detect physical tumors because it cannot see structure. No one screening test is 100% accurate, but combining these screening tests greatly increases the chance of early detection and the opportunity to intervene early and change the outcome.
No. Any hormonal changes are systemic and do not alter the temperature differentials or patterns in a thermogram.
Prevention is the key to maintaining good health. Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging of the body or a specific body part can aid in the detection, diagnosis and prognosis of disease as well as monitor therapy progress. Thermal scans are valuable in the early detection of arthritis, diabetes, heart disease, stroke, immune system dysfunction, breast disease and other disorders. They are able to view inflammation and visualize pain. This is particularly useful for someone who cannot find the origin of their pain. Thermal findings related to various organs can allow for early warning signs and treatment for areas of concern before they become more serious problems. The information is very useful for further diagnostics and for the treating healthcare practitioner. Many conditions as well as areas of pain or injury can be visualized using Thermography, such as:
| Neck & Back Problems | Artery Inflammation | Sprain/Strain |
| Arthritis | Vascular Disease | Stroke Risk |
| Headaches | Breast Disease | Whiplash |
| Nerve Damage | Carpal Tunnel Syndrome | Diabetes |
| Unexplained Pain | Disc Disease | Nervous System Disorders |
| Fibromyalgia | Inflammatory Pain | Breast Screening |
| RSD | Skin Cancer | Referred Pain Syndrome |
| TMJ Conditions | Metabolic Disorders | Vascular Disorders |
| Soft Tissue Injuries | Raynaud’s | And Much More�? |
Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging is very reasonable considering the sophistication of the technology involved. Our fee includes your consultation, thermal images, the Medical Doctor’s interpretation of the images, and a mailed copy of the doctor’s written report and color images. We will also mail a copy of your results to your healthcare provider at no additional cost.
Our fee for a breast thermogram is $195. A three month follow up breast thermogram is $150. A Region of Interest is $195, half body images are $295 and full body images are $395.
Some insurance carriers cover thermal imaging. Please contact your individual provider for your specific plan allowances. Health Savings Accounts, cafeteria plans and wellness plans normally pay for thermograms. We are able to provide you with a billing code and receipt to submit to your insurance company for reimbursement. Our policy is to receive payment at the time of service. For your convenience, we accept cash, personal check, VISA, MasterCard, AMEX and Discover.
The United Breast Cancer Foundation may reimburse up to $300 for two thermograms three months apart, depending on their current available funding. Visit www.ubcf.info and click on the thermogram picture in the top left corner of the website that has “free breast screening‿written above it. Follow their application instructions for reimbursement.
The insurance billing code for Thermography is 93740
Thermal images are colorful. The colors in a thermogram are applied to ranges in temperature and they identify patterns. The patterns are more important than the colors. White represents the hottest temperature, moving down into the reds, oranges, yellows and greens. Blues represent the cooler temperatures. Below are some examples of thermal images.

EXTENT OF INJURY — Football player with a stress fracture that was not detected with x-ray. Bone scan confirmed Thermography findings.
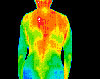
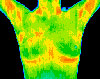
BACK, NECK AND HEADACHE PAIN — Pain patterns are visible on a Thermal Scan, enabling you to begin targeted care.

DENTAL ISSUES — Thermography findings helped confirm diagnosis of TMJ and referral to the appropriate specialist for treatment.

UNEXPLAINED PAIN — Thermal Scans detected the vascular disease that was causing this patient’s inflammatory pain.
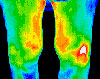
ARTHRITIS — Arthritis generally appears as “hot areas,‿since the affected sites are inflamed. Thermal Scans can detect early signs of arthritis, and differentiate between Osteo and Rheumatoid.

NORMAL BREAST THERMOGRAM — Good thermal symmetry with no suspicious thermal findings. These patterns establish a baseline against which future scans can be compared to detect any changes.
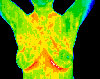
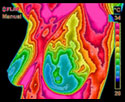
FIBROCYSTIC BREAST DISEASE — Significant vascular activity in the left breast which was clinically correlated with fibrocystic changes.
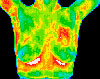
DUCTAL CARCINOMA — Vascular asymmetry in the upper left breast was particularly suspicious and clinical investigation indicated a palpable mass. Biopsy confirmed a DCIS of 2cm.
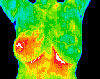
INFLAMMATORY CANCER — This cancer cannot be detected by mammogram because it is not a “lump‿cancer. Prior to the Thermogram, there were no signs of abnormality.
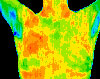
BASELINE THERMOGRAM — Baseline thermogram showed a slight hyperthermic asymmetry in the upper right breast.
THREE MONTHS — The follow-up study at 3 months showed the pattern had become more well defined. Mammography was inconclusive.

TWELVE MONTHS — Significantly increased vascular changes. Repeat mammogram showed a small calcification (1mm).